
MedTech trends and challenges in 2023
In this article let us explore the three key trends that are shaping the future of the medical technology industry, as well as challenges posed to the market and investors in 2023.
10 min read
In this Article:
- The increasing consumer adoption of telemedicine
- The enhancement to healthcare processes brought by artificial intelligence
- Medical robots gaining real traction on the market
- Challenges posed by deglobalization, investment downturn and staffing shortages
According to Statista, the current value of the MedTech market is around $19.65 billion, and it is expected to reach $22.84 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 3.83%. Going forward into 2023, and by analyzing trends in technology and investment capital of recent years, we can safely forecast three main areas that will generate growth in the MedTech industry. The increasing consumer adoption of Telemedicine, the enhancement to healthcare processes brought by artificial intelligence, and the gained traction of medical robots.
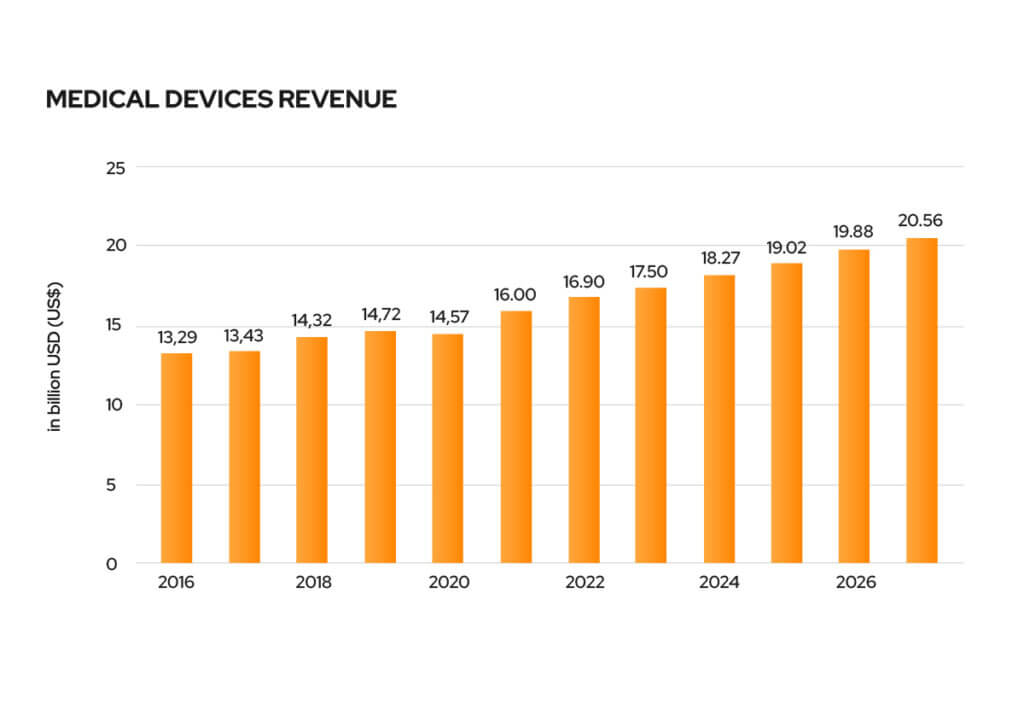
Promising trends of 2023
The emergence of COVID-19 led to significant shifts in consumer behavior, and the healthcare industry was not exempt. McKinsey’s survey indicates that in 2019, only 11% of US consumers used telehealth services. However, as a result of the pandemic, that number surged to 46%.
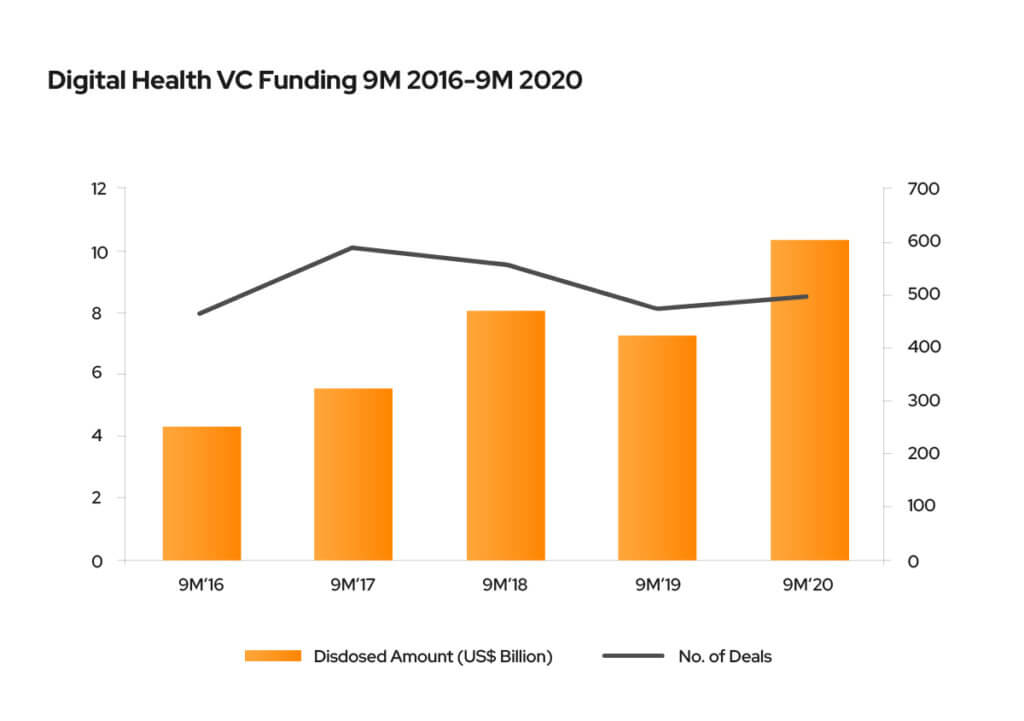
It appears that telemedicine will continue to be a growing trend even after the situation returns to normalcy, with 76% of US consumers expressing their interest in utilizing telehealth as a complementary service to in-person doctor visits. The telehealth sector has attracted significant attention from VCs, with a projected CAGR of more than 23% from 2020-2026. In 2019, telemedicine startups received nearly $1.8 billion in VC funding, while VCs invested $3.2 billion in companies in the telemedicine space in just a nine-month span in 2020.
Research by CB Insights indicates that healthcare AI funding across 121 deals reached $2.1 billion in Q3 2020. The FDA has been receptive to artificial intelligence and has plans to update regulatory frameworks specific to AI. By early 2020, there were already 64 AI/ML-based medical devices and algorithms that were FDA-approved. AI applications in healthcare have the potential to save the European healthcare system €200 billion annually (including opportunity costs), according to Deloitte’s European study with MedTech Europe.
Medical diagnostics are an AI application that seems to generate the most promise. Commercial applications for image recognition AI technology in medical diagnostics are already available, and the market is projected to exceed $3 billion by 2030, according to an IDTechEx report.
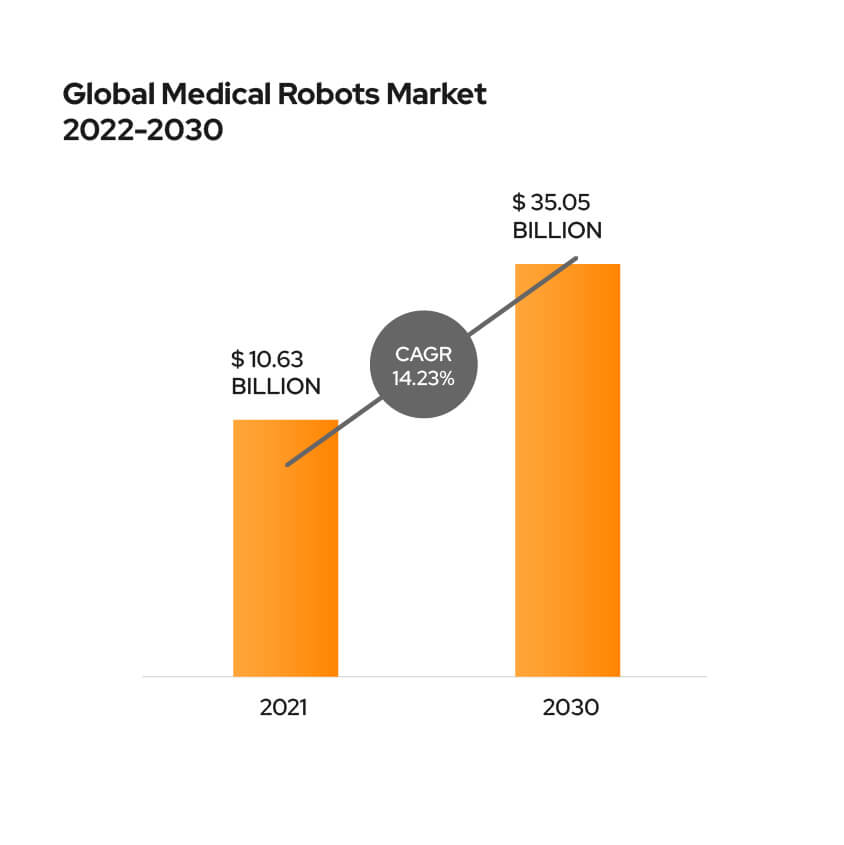
The worldwide market size of medical robots is projected to reach $35.05 billion by 2030, according to a report by Verified Market Research.
Surgical robots are the leading category of robotics used in healthcare, and demand for surgical robot technology has seen significant growth in recent years. Despite a substantial decrease in the number of elective surgeries due to the pandemic, investments in robotic surgery companies have been one of the primary drivers of VC funding in the medical devices category. Moreover, many experts claim that the use of robotic technology is particularly useful during the recent and any future pandemics, as it helps to reduce human physical contact.
Challenges and market dynamics in 2023
However, in 2023 new uncertainties are emerging, despite the optimism generated by new technologies and the gradual recovery from the disruptions of COVID-19. These challenges include staffing shortages, investment downturns, market disruptions and deglobalization. As a result, MedTech players require even more agility and foresight to adapt to an increasingly dynamic global industry.
Deglobalization and reshoring are becoming increasingly prevalent and are impacting the entire value chain of the MedTech industry. The global trade-to-GDP ratio, a commonly used indicator for globalization measured by the World Bank, has decreased from 61% in 2008 to 57% in 2021, with an expected smaller outcome for 2022 due to trade restrictions between the U.S. and China, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the Russia-Ukraine conflict. These factors have highlighted the importance of maintaining adequate stocks of critical components and raw materials, as well as having a well-diversified supplier base.
Manufacturers are likely to focus on expanding supplier diversification and stockpiling efforts; however, there are limits to these initiatives. If the current global trade environment persists, governments and market players may turn to “near-shoring” or “friend-shoring” to benefit certain regions as production and logistics hubs become based on proximity and/or geopolitical alliances. Alternatively, the fragmentation of the global market may lead to increased regional integration, causing manufacturers to further regionalize their production and supply chains.
The MedTech investment downturn will affect regions differently, with unique challenges in each area. Despite this, MedTech firms must quickly adapt and find ways to drive innovation and investment, such as through cross-sector partnerships and collaboration with academia. The downturn is not level and impacts regions differently, and as such requires unique approaches in every market. In the Asia-Pacific region, China dominated MedTech investment in 2021, but investment activity is expected to slow down, and the focus will shift away from pandemic-related topics to those that improve access, affordability, and quality of healthcare. In the United States, M&A deals and venture capital investments have dropped sharply from 2021 peak levels, although many investors remain optimistic. In Germany, where a significant portion of MedTech sales are driven by products under three years old, an innovation slowdown could have lasting consequences for the previously flourishing Berlin health-tech startup scene. In the United Kingdom, healthcare staff shortages have led to a diversion of investments away from technology and toward other areas, making it more challenging for MedTech to drive revenue channels and cost savings.
To address the growing shortage of healthcare professionals, healthcare providers are turning to MedTech for help through communication and automation innovations. Like the UK, the US also experienced a sharp drop in the labor pool of nurses in 2021, and there is currently a general shortage of primary care providers in many areas. To increase the efficiency of their staff, healthcare providers will rely more on MedTech manufacturers to provide tools that reduce administrative and labor burdens. Medical devices will need to be even more seamlessly integrated with electronic health records and mobile devices, allowing for virtual support from specialists and automated tools to make care teams more efficient and flexible. Additionally, advances in artificial intelligence and clearer regulatory guidance will make it easier to introduce tools that automate patient data analysis, triage, and monitoring, ultimately enabling healthcare providers to deliver quality care more sustainably with fewer staff. The shortage is expected to impact the consumer market as well, with products that allow a patient to self-care or self-diagnose, and the market will require proven methods of driving the adoption of such devices and solutions.
In 2022, Direct-to-Consumer (DtC) advertising proved its effectiveness in driving the adoption of medical devices, particularly those that patients use directly or compete with pharmaceuticals, according to IQVIA researchers. This trend was evident with companies such as Abbott Laboratories, Cue Health, and Hologic airing national TV ads, and was not limited to the U.S, with Insulet running ads in other countries. As more medical devices are introduced as alternatives to pharmaceutical treatments, DtC advertising will also be crucial in raising consumer awareness. It is therefore safe to assume that In 2023, DtC advertising will continue to be a powerful driver for medical devices.
To summarize, the MedTech industry faces many uncertainties in 2023, and manufacturers must be more agile and proactive in adapting to the changing industry landscape. The challenges are shared between the industry and healthcare providers, which means they will rely on MedTech for innovations in communication, automation, and staff efficiency. As a direct result of the challenges faced by healthcare providers, patients are suffering a diminishing quality of service, and will likewise look to MedTech for a relief. To face this reliance, the MedTech industry must continue to innovate and find new ways to adapt to challenges and uncertainties and provide innovative solutions to both healthcare providers and consumers.




